Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of 3D modeling and learn how it shapes various industries, from architecture to gaming. This captivating guide highlights the significance of 3D modeling, introduces popular software, and explains fundamental and advanced techniques. Join us on a journey that will inspire and equip you with the knowledge to create stunning 3D models!
Uncover the transformative power of 3D modeling, as we delve into the importance of this technology and its diverse applications. Follow a clear path through the pros and cons of popular software, understand fundamental and advanced techniques, and explore various file formats.
Ultimately, grasp the future potential of 3D modeling and its significant role in industries worldwide.
Introduction to 3D Modeling
3D modeling is the process of creating a mathematical representation of a three-dimensional object or environment, using specialized software. It involves manipulating vertices, edges, and faces in a virtual space, resulting in a digital replica that can be rotated, scaled, and otherwise adjusted to fit specific needs.
Importance of 3D Modeling
3D modeling plays a crucial role in several industries, from manufacturing and entertainment to architecture and healthcare. Its primary benefits include:
- Enhanced visualization: By creating detailed 3D models, professionals can better visualize and understand complex systems or designs.
- Efficient prototyping: 3D models can be used as prototypes before actual manufacturing, helping to identify and address potential issues early on.
- Reduced costs: Through the use of virtual prototyping, companies can save significant amounts of time and money that would otherwise be spent on physical prototypes and revisions.
Applications of 3D Modeling
3D modeling is an essential tool in numerous sectors:
- Manufacturing:Companies use 3D modeling to design, optimize, and test products and components before production.
- Entertainment:Film, television, and gaming industries rely on 3D modeling for character creation, set design, and visual effects.
- Architecture:Architects and designers use 3D modeling to create detailed building plans, conduct simulations, and present projects to clients.
- Medicine:Medical professionals employ 3D modeling for surgical planning, prosthetic design, and drug development.
- Engineering:Engineers use 3D modeling for infrastructure planning, structural analysis, and environmental impact assessments.
3D Modeling Software
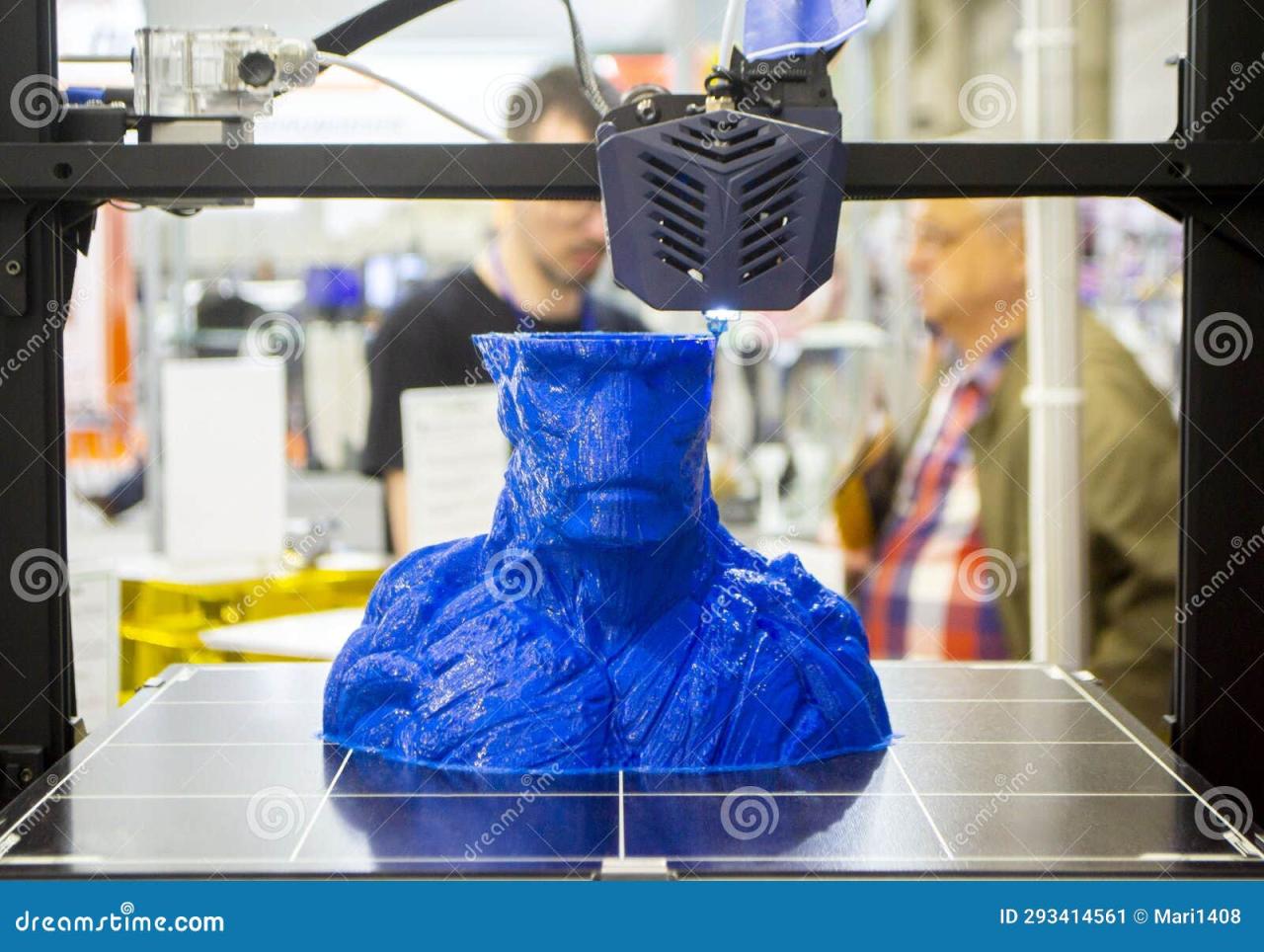

Once you’ve grasped the basics of 3D modeling, it’s essential to choose the right software for your projects. Various 3D modeling software options are available, each with unique features, advantages, and disadvantages. This guide will introduce you to some of the most popular 3D modeling software and help you decide which one is the best fit for your needs.
Blender
- Features:Blender is a powerful, open-source 3D modeling software with a comprehensive suite of tools for modeling, rigging, animation, rendering, and compositing. It supports polygon, NURBS, metaballs, and curves, and its extensive library of plugins further expands its capabilities.
- Pros:
- Open-source and free.
- Strong community support.
- Rich feature set, including robust sculpting capabilities.
- Cons:
- Steep learning curve.
- UI may feel overwhelming for beginners.
- Rendering performance may not be as strong as some paid alternatives.
Autodesk Maya
- Features:Autodesk Maya is a high-end, feature-rich 3D modeling software used widely in the film, TV, and gaming industries. It excels in character modeling and animation, and its Arnold renderer and Bifrost fluid dynamics simulation toolset are powerful additions.
- Pros:
- Industry-standard software.
- Strong animation and rigging features.
- Effective polygon and NURBS modeling tools.
- Cons:
- Expensive, especially for individual users.
- Complex UI may intimidate beginners.
- Requires a powerful computer to run smoothly.
Autodesk 3ds Max
- Features:Autodesk 3ds Max is primarily used for architectural visualization, game development, and television commercial production. It has advanced modeling tools, Arnold renderer support, and a robust particle and physics simulation system.
- Pros:
- Strong modeling, texturing, and rendering capabilities.
- Dynamic simulation and animation tools.
- Support for third-party plugins and scripts.
- Cons:
- Expensive, like other Autodesk products.
- Windows-only software.
- Limited character animation capabilities compared to Maya.
Cinema 4D by Maxon
- Features:Cinema 4D is a versatile 3D modeling software popular among artists and motion designers. It offers robust modeling, texturing, animation, and rendering tools and has a user-friendly interface that allows users to grasp its features quickly.
- Pros:
- User-friendly interface and intuitive navigation.
- Impressive rendering capabilities with the Physical Renderer.
- Strong motion graphics and animation features.
- Cons:
- Less powerful modeling tools than some competitors.
- Limited third-party plugin ecosystem.
- Can be pricey for individual users.
3D Modeling Techniques
3D modeling is the process of creating a three-dimensional representation of an object or a surface using specialized software. This process involves a variety of techniques, both basic and advanced, that can help you create more detailed and realistic models.
Let’s explore some of these techniques, along with step-by-step procedures and examples.
Basic Techniques
Basic 3D modeling techniques include the following:
- Extrusion:This technique involves pushing or pulling a 2D shape into 3D space. Imagine taking a flat piece of paper and pushing it forward, creating a 3D object.
- Revolution:Using this technique, you can rotate a 2D shape around an axis, creating a 3D object. An example of this technique is creating a cylinder by revolving a rectangle around its central axis.
- Lathe:Lathe is similar to revolution, but instead of a straight line, a curved shape is used to create the 3D object. This is often used for creating objects like wheels, cones, and goblets.
Advanced Techniques
Advanced 3D modeling techniques include the following:
- Subdivision:Subdivision involves dividing a 3D object into smaller, more detailed parts, allowing artists to create complex shapes with a smooth surface. It can be used to add organic detail to characters, creatures, and hard-surface models.
- Boolean operations:Boolean operations involve combining, subtracting, or intersecting two or more 3D objects to create a new 3D model. This technique is used to create complex objects from simpler ones.
- NURBS surfaces:Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines (NURBS) are mathematical representations of curves and surfaces. They are used to create smooth and complex shapes for engineering and industrial design.
Step-by-Step Procedures
Let’s take a look at the step-by-step procedures for both basic and advanced techniques:
- Start by opening your 3D modeling software and creating a new project.
- Choose the appropriate tool or method based on the desired 3D modeling technique:
- For extrusion, use the “push/pull” or “extrude” tool and select the 2D shape you want to push into 3D space.
- For revolution, use the “rotate” tool with the “axis” or “revolution” option and select the 2D shape you want to revolve.
- For lathe, use the “lathe” tool and select the 2D curve or profile you want to revolve around the central axis.
- Create the 3D object using the chosen technique.
- Fine-tune and adjust the 3D model, if needed, by using the available tools in your 3D modeling software and applying the advanced techniques as needed.
- Save and export the finished 3D model, and optionally, render a final image for presentation.
Illustrative Examples
Here are some illustrative examples for each technique:
- Extrusion:Imagine taking a rectangular piece of paper and pushing it forward, creating a box. This is an example of an extrusion technique.
- Revolution:Imagine rotating a circle around its central axis, creating a sphere. This is an example of the revolution technique.
- Lathe:Imagine creating a vase by rotating the cross-section of a circle, moving it up & down or sideways, around the central axis. This demonstrates the lathe technique.
- Subdivision:Take a simple 3D object such as a cube and divide it into smaller, more detailed parts, like a character’s facial features. Apply subdivision techniques to create smoother, more complicated shapes.
- Boolean operations:
Imagine combining a sphere with a cylinder to create a drinking glass. First, you would use a boolean operation to intersect the cylinder with the sphere, resulting in a hollowed-out region. Then, use another boolean operation to subtract the smaller cylinder from the sphere, leaving you with a complete drinking glass.
- NURBS surfaces:Consider creating a smooth, flowing shape such as a car body. These shapes can be built using the NURBS technique, which allows artists and designers to control complex curves and surfaces with precision and accuracy.
These basic and advanced techniques help you create various 3D models for different purposes. With practice and the right tools, these techniques will allow you to create highly detailed and realistic models.
3D Modeling Formats
3D modeling formats are crucial for saving and sharing 3D models. Each format has unique features that cater to specific needs. Understanding these formats can make a significant difference in selecting the right one for your project.
OBJ
Object File
Object File
OBJ is a simple data-format that represents 3D geometry. It is widely used and supported by many 3D software applications. OBJ files store geometry, vertex normals, and texture vertex coordinates.
- Pros: Widely supported and human-readable.
- Cons: Doesn’t support materials or complex scenes.
STL
Stereolithography
Stereolithography
STL is the standard file format for 3D printing. It represents a 3D model’s surface geometry as a mesh of triangles. STL files don’t support color or texture.
- Pros: Used in 3D printing and CAD software.
- Cons: Limited to triangular meshes and doesn’t support color or texture.
FBX
FilmBox
FilmBox
FBX is a proprietary file format developed by Autodesk for 3D animation and game development. It stores geometry, animation, materials, and camera information.
- Pros: Supports complex scenes and various data types.
- Cons: Requires a commercial license and can be resource-intensive.
GLTF/GLB
GL Transmission Format
GL Transmission Format
GLTF/GLB is a standard for 3D scenes and models. It is designed for efficiency and real-time rendering. It supports geometry, materials, textures, and animations in a compact JSON format.
- Pros: Efficient and supports complex scenes.
- Cons: Limited software support compared to OBJ or FBX.
Conversion Guide
Converting between formats can be achieved using 3D modeling software or online converters. Choose software that supports the formats you need. Online converters are convenient but may lack advanced features or pose security risks.
3D Modeling for Specific Industries
3D modeling is a versatile tool, widely used in a range of industries for various purposes. Its ability to create realistic and manipulable objects makes it an invaluable asset in fields such as architecture, product design, and film and game production.
Here, we delve into these specific applications, providing examples and explanations.
Use of 3D modeling in Architecture
In architecture, 3D modeling is used for a variety of purposes, from initial design to final construction. It allows architects to visualize their designs in three dimensions, enabling them to identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments before construction begins.
This can save time and money, as well as reducing the risk of errors during the building process.
-
Building Information Modeling (BIM): This is a process that involves creating and managing digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of places. It enables architects to create a digital model of a building, which can be used throughout the design, construction, and maintenance process.
BIM can include information about the building’s materials, systems, and components, making it a powerful tool for managing complex projects.
-
Virtual Walkthroughs: 3D modeling can be used to create virtual walkthroughs of buildings, allowing architects, clients, and stakeholders to explore the design in a realistic, immersive way. This can help to identify any issues with the design, as well as giving clients a better understanding of the final product.
-
3D Rendering: 3D models can be rendered to create realistic images or videos of the finished building. These can be used for presentations, marketing materials, or planning applications.
Application of 3D modeling in Product Design
In product design, 3D modeling is used to create detailed, accurate representations of products. This can help to identify any potential issues with the design, as well as allowing designers to test and refine the product before it goes into production.
3D modeling can also be used to create prototypes, which can be tested and refined before the final product is manufactured.
-
Parametric Design: This is a design approach that uses parameters to define the design. These parameters can be changed, allowing the designer to easily modify the design. This is particularly useful in product design, where changes may need to be made due to manufacturing constraints or user feedback.
-
Rapid Prototyping: 3D modeling can be used to create rapid prototypes, which can be tested and refined before the final product is manufactured. This can save time and money, as well as reducing the risk of errors during the manufacturing process.
-
Product Visualization: 3D models can be used to create accurate visualizations of products. These can be used for presentations, marketing materials, or user manuals.
Examples of 3D modeling in Film and Game Production
In film and game production, 3D modeling is used to create characters, objects, and environments. This can range from simple models to complex, detailed characters and environments. 3D modeling can be used for both pre-visualization (pre-vis) and final production.
-
Pre-visualization: 3D models can be used to create rough drafts of scenes, allowing directors and cinematographers to plan shots and sequences before filming begins. This can help to save time and money during the filming process.
-
Character Creation: 3D models can be used to create detailed characters. These models can be animated, allowing for realistic movement and expression.
-
Environment Creation: 3D models can be used to create detailed environments, from simple rooms to complex cityscapes. These environments can be rendered to create realistic backgrounds for live-action films, or used as the setting for animated films and games.
Future of 3D Modeling
3D modeling has come a long way since its inception and it continues to evolve at a rapid pace. With advancements in technology, we are witnessing new trends and possibilities that are shaping the future of 3D modeling. However, these advancements also bring forth challenges that need to be addressed for 3D modeling to reach its full potential.
Latest Trends in 3D Modeling
-
Real-time Rendering: With the help of technologies like Unreal Engine and Unity, real-time rendering has become a game-changer in the field of 3D modeling. It allows designers to see their changes instantly, reducing the time and effort required for iteration.
-
Artificial Intelligence: AI is making its way into 3D modeling in various ways. Machine learning algorithms are being used to automate tasks such as mesh creation and texture mapping, making the process faster and more efficient.
-
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR are revolutionizing the way we interact with 3D models. These technologies allow designers to visualize their models in a real-world environment, enhancing the design and decision-making process.
Challenges in the Advancement of 3D Modeling
-
Complexity and Detail: As the demand for more realistic and intricate 3D models increases, so does the complexity of creating them. This can lead to longer production times and higher costs.
-
Data Management: With the increased use of real-time rendering and AI, the amount of data generated in the 3D modeling process is growing exponentially. This poses challenges in terms of storage, processing power, and data management.
-
Accessibility and Usability: While 3D modeling software has become more user-friendly, there is still a steep learning curve for beginners. Additionally, the high cost of software and hardware can be a barrier for many individuals and small businesses.
Potential of 3D Modeling in the Future
-
Digital Twin Technology: The future of 3D modeling lies in creating digital twins – virtual replicas of physical products or systems. These twins can be used for a variety of purposes, such as predictive maintenance, training, and product optimization.
-
Integration with IoT: With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), 3D modeling will become even more interconnected and data-driven. This will enable real-time monitoring and analysis of products and systems, leading to improved performance and efficiency.
-
Democratization of 3D Modeling: As software and hardware become more affordable and user-friendly, the barriers to entry for 3D modeling will decrease. This will lead to a wider adoption of the technology and a surge in creativity and innovation.
Wrap-Up
With a solid understanding of 3D modeling fundamentals, advanced techniques, and future trends, you’re now prepared to join the creative revolution. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned developer, harnessing the art of 3D modeling will elevate your skills and unleash new potential in your projects.
Embrace the challenge and amplify your creative impact!