Glass railings have become a popular choice for enhancing the aesthetic appeal and safety of outdoor spaces. Their sleek, modern designs seamlessly integrate with various architectural styles, offering unobstructed views and a sense of openness. This guide delves into the diverse world of outdoor glass railings, exploring different types of glass, design considerations, installation techniques, and crucial safety aspects.
We’ll cover everything from choosing the right glass and frame materials to ensuring compliance with building codes and maintaining the longevity of your investment.
From the practical considerations of durability and maintenance to the aesthetic impact on your property’s overall design, we aim to provide a thorough understanding of this increasingly popular architectural feature. Whether you’re a homeowner planning a renovation or a professional installer, this comprehensive guide offers valuable insights and practical advice to help you make informed decisions.
Types of Glass Railings for Outdoor Use
Choosing the right glass for an outdoor railing involves considering factors like strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. The type of glass selected will significantly impact the overall longevity and safety of the railing system. Different glass types offer varying levels of resistance to impact, thermal stress, and weathering.
Types of Glass for Outdoor Railings
Several types of glass are suitable for outdoor railing applications, each possessing unique properties. Tempered glass, laminated glass, and insulated glass units (IGUs) are the most common choices. Tempered glass undergoes a heat treatment process that increases its strength significantly compared to annealed (standard) glass.
This makes it far more resistant to impact and thermal shock, crucial for outdoor use where it’s exposed to fluctuating temperatures and potential impacts. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with a layer of interlayer material, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB).
This interlayer adds significant strength and safety; even if the glass breaks, the fragments adhere to the interlayer, preventing shattering and reducing the risk of injury. Insulated glass units (IGUs) are composed of two or more panes of glass separated by a spacer filled with a desiccant and an inert gas like argon.
This design improves energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer and noise transmission, a beneficial feature in certain climates.
Frameless vs. Framed Glass Railing Systems
The choice between frameless and framed glass railing systems largely depends on aesthetic preferences and structural considerations. Frameless systems offer a sleek, minimalist look, maximizing the view and creating an unobstructed visual experience. These systems rely on strong glass panels and specialized hardware for support, often using spigots or clamps to secure the glass to posts.
A common example of a frameless system would be a glass railing on a balcony where the glass panels are directly mounted to the supporting structure, creating a clean, modern appearance. Conversely, framed glass railing systems incorporate a metal or other material frame around the glass panels, providing additional structural support and a more traditional aesthetic.
These systems can be more robust and easier to install, offering a variety of design options. A framed system might be preferred for a deck railing where a more substantial and visible frame complements the overall design.
| Material | Cost | Maintenance | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tempered Glass | Medium to High | Low; occasional cleaning | High; resistant to impact and thermal shock |
| Laminated Glass | High | Low; occasional cleaning | Very High; enhanced safety and impact resistance |
| Insulated Glass Units (IGUs) | High | Low; occasional cleaning | High; improved energy efficiency and sound insulation |
Design Considerations for Outdoor Glass Railings
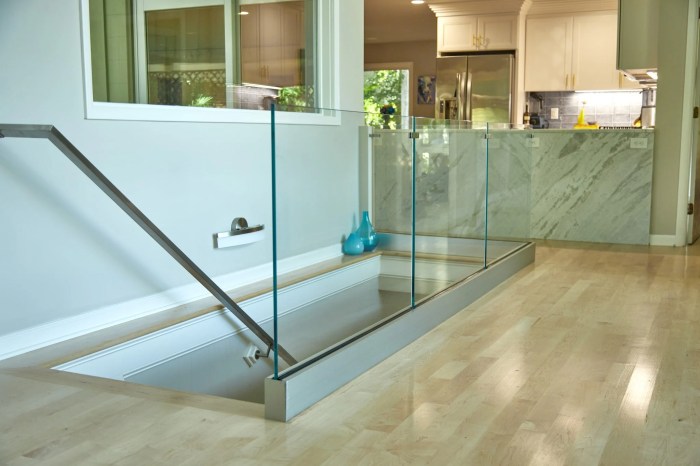

Designing safe and aesthetically pleasing outdoor glass railings requires careful consideration of several factors. The choice of glass thickness, railing post materials, and overall system design significantly impact both the structural integrity and the visual appeal of the finished product.
Adherence to relevant building codes and safety standards is paramount to ensure the railing’s ability to withstand expected loads and provide adequate protection.
Glass Thickness and Structural Integrity
The thickness of the glass used directly affects the railing’s safety and structural integrity. Thicker glass offers greater strength and resistance to impact and bending forces. Building codes typically specify minimum glass thicknesses based on the height and intended use of the railing.
For example, a balcony railing at a significant height will require thicker glass than a low deck railing. Common glass thicknesses range from ½ inch to 1 inch, with laminated or tempered glass preferred for outdoor applications due to their enhanced strength and safety features.
Tempered glass, when broken, shatters into small, relatively harmless pieces, minimizing the risk of injury. Laminated glass, composed of two or more layers bonded together with a polymer interlayer, holds together even when broken, providing added safety. Failure to meet these minimum thickness requirements can lead to structural failure and potential injury, making adherence to local building codes and relevant safety standards like those from ASTM International (American Society for Testing and Materials) crucial.
Railing Post Materials and Compatibility with Glass
The choice of railing post material significantly influences the overall aesthetic and structural performance of the glass railing system. Common materials include metal (stainless steel, aluminum, wrought iron), wood (treated lumber, cedar, redwood), and composite materials. Each material offers different advantages and disadvantages regarding durability, maintenance, and aesthetic compatibility with glass.
- Stainless Steel:Offers excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and a modern aesthetic. It pairs well with clear or tinted glass, creating a sleek, contemporary look.
- Aluminum:A lighter-weight option than stainless steel, aluminum is also corrosion-resistant and relatively inexpensive. It can be powder-coated in various colors to complement different design styles.
- Wrought Iron:Provides a more traditional, ornate look. Its strength and durability make it a suitable choice for heavier glass panels, but it requires regular maintenance to prevent rust.
- Wood:Offers a natural, warm aesthetic. Treated lumber or naturally rot-resistant woods like cedar or redwood are essential for outdoor applications. Wood posts require regular maintenance to prevent decay and insect damage.
- Composite Materials:These materials offer a blend of the benefits of wood and metal, often being low-maintenance and durable. They can be designed to mimic the look of wood or metal, providing flexibility in design choices.
Aesthetically pleasing combinations often involve contrasting materials. For example, sleek stainless steel posts paired with clear glass create a minimalist modern look, while warm wood posts with frosted glass offer a more traditional, inviting feel.
Examples of Glass Railing Systems for Different Applications
Below are three examples illustrating different glass railing system designs for a deck, balcony, and staircase.
- Deck Railing:This system uses ½-inch tempered glass panels held in place by stainless steel balusters and top and bottom rails. The stainless steel is brushed for a contemporary look, complementing the clean lines of the glass. The overall aesthetic is minimalist and modern.
- Balcony Railing:This design incorporates ¾-inch laminated glass panels supported by powder-coated aluminum posts in a dark bronze finish. The darker posts provide a visual contrast to the glass, creating a sophisticated and elegant feel. The laminated glass enhances safety due to its shatter-resistant properties, suitable for a higher-risk application like a balcony.
- Staircase Railing:This system utilizes ¼-inch thick tempered glass panels attached to a robust wrought iron framework. The wrought iron is intricately designed with decorative scrolls and flourishes, creating a classic and ornate look. The glass provides a sense of openness while maintaining safety.
Installation and Maintenance of Outdoor Glass Railings
Proper installation and consistent maintenance are crucial for ensuring the longevity, safety, and aesthetic appeal of your outdoor glass railing system. Neglecting either can lead to costly repairs or even safety hazards. This section details the process of installing a frameless glass railing system and provides guidance on maintaining its pristine condition.
Frameless Glass Railing System Installation
Installing a frameless glass railing system requires precision and attention to detail. Improper installation can compromise safety and structural integrity. The following steps Artikel a typical installation process, but always consult the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific system.
- Preparation and Planning:Begin by carefully measuring the area where the railing will be installed. Accurate measurements are paramount for proper fitting and avoiding material waste. Ensure the surface is level and free of debris. Mark the locations for post anchors.
- Post Installation:Securely install the posts using appropriate anchors for your chosen surface (concrete, wood, etc.). Ensure the posts are plumb and level, using a level and plumb bob for accuracy. Over-tightening can crack the posts, while under-tightening compromises stability.
- Glass Panel Preparation:Carefully handle the glass panels, using gloves to prevent fingerprints and scratches. Inspect each panel for any damage before installation. Apply protective film to the glass surfaces to prevent scratching during installation.
- Glass Panel Installation:Using appropriate clamps and spacers, carefully position the glass panels between the posts. Ensure the panels are aligned correctly and that there is consistent spacing between them. This is critical for a uniform appearance and structural integrity.
- Hardware Installation:Secure the glass panels to the posts using the specified hardware. This typically involves using clamps, channel systems, or other specialized fasteners. Ensure the hardware is properly tightened to secure the glass panels without over-tightening, which could cause breakage.
- Final Inspection:After installation, conduct a thorough inspection of the entire railing system. Check for any loose hardware, misaligned panels, or other issues. Ensure the railing meets all safety standards and local building codes.
Tools and Materials:Necessary tools and materials will vary depending on the specific system, but typically include: measuring tape, level, plumb bob, drill, appropriate drill bits, anchors, posts, glass panels, spacers, clamps, hardware, safety glasses, work gloves.
Cleaning and Maintenance of Outdoor Glass Railings
Regular cleaning and maintenance are vital for preserving the beauty and structural integrity of your outdoor glass railing. Different glass types may require slightly different cleaning methods.
Cleaning Methods:For most glass railings, a simple solution of warm water and mild dish soap is sufficient. Apply the solution using a soft cloth or sponge, avoiding abrasive cleaners or scouring pads that can scratch the glass. Rinse thoroughly with clean water and dry with a lint-free cloth.
For tougher stains, consider using a glass cleaner specifically designed for outdoor use. Always test any cleaning product on a small, inconspicuous area first to ensure it doesn’t damage the glass or finish.
Specific Glass Types:Tempered glass, commonly used in railings, is durable but can be susceptible to etching from harsh chemicals. Laminated glass offers added safety and is generally more resistant to damage. Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific cleaning instructions for your type of glass.
Potential Problems and Solutions
Several issues can arise with outdoor glass railings over time. Addressing these problems promptly can prevent further damage and ensure the safety and longevity of the railing.
- Cracking or Chipping:This can be caused by impact, improper installation, or stress from temperature fluctuations. Repair is usually not possible; replacement of the damaged panel is necessary.
- Leaks:Leaks can occur if the sealant around the posts or between panels fails. Repair involves removing the old sealant, cleaning the surface, and applying a new high-quality sealant specifically designed for outdoor use.
- Corrosion:Metal components, such as fasteners, can corrode over time due to exposure to the elements. Regular inspection and replacement of corroded parts is crucial to prevent structural failure. Consider using stainless steel hardware for increased corrosion resistance.
- Water Spotting:Hard water can leave unsightly spots on the glass. Regular cleaning with a suitable glass cleaner and a squeegee can help prevent this.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
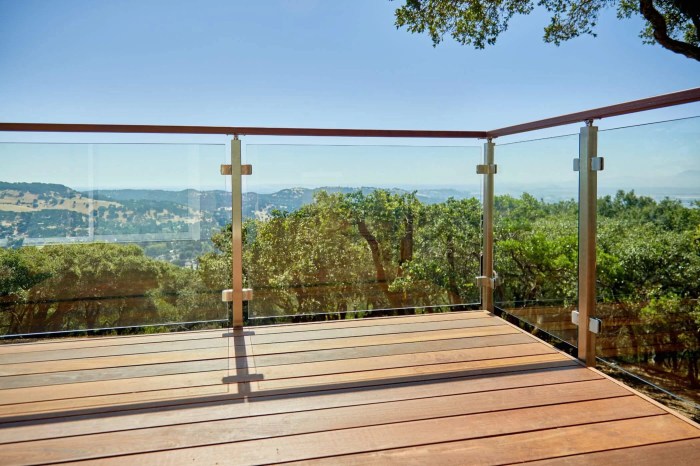

Outdoor glass railings, while aesthetically pleasing, must prioritize safety and adhere to stringent building codes. Modern designs incorporate several features to mitigate risks, while regulations ensure structural integrity and user protection. Understanding these aspects is crucial for both designers and installers.
Modern glass railing systems employ a range of safety features to minimize the risk of injury. Laminated glass, for instance, consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with a strong interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB). This interlayer holds the glass fragments together even if the glass breaks, preventing sharp shards from falling and causing harm.
Furthermore, impact-resistant coatings can be applied to the glass to further enhance its durability and resistance to damage from impacts. These coatings can also offer protection against UV degradation, maintaining the clarity and strength of the glass over time.
Stainless steel or aluminum posts and fittings provide robust support, and careful design ensures that the railing’s structure can withstand significant forces.
Building Codes and Regulations for Outdoor Glass Railings
Building codes and regulations governing outdoor glass railings vary by location, but common requirements focus on height, strength, and spacing. These regulations are designed to prevent falls and ensure the railing’s ability to withstand anticipated loads, such as wind and snow.
For example, the International Building Code (IBC) often specifies minimum railing heights, typically 42 inches (1067 mm) above the walking surface for residential applications, with specific requirements for other contexts like balconies and decks. The code also dictates requirements for the strength of the railing system, often expressed in terms of load capacity in pounds per linear foot (plf) or kilopascals (kPa), and spacing between balusters or glass panels, usually limited to a maximum gap to prevent accidental falls.
Calculating Glass Thickness and Post Spacing
Determining appropriate glass thickness and post spacing involves several factors, most importantly wind load and snow load. These loads vary significantly based on geographic location, building height, and exposure to the elements. For example, a coastal area exposed to high winds will require thicker glass and closer post spacing compared to a sheltered inland location.
Engineering calculations are often necessary to determine the required glass thickness and post spacing to ensure compliance with local building codes. These calculations usually involve sophisticated software or engineering expertise. A simplified example might involve using a formula that considers the glass’s tensile strength, the anticipated wind pressure, and the distance between support posts to determine a minimum thickness to prevent breakage under load.
A similar approach would be used for snow load calculations, where the weight of accumulated snow is considered a primary factor. The precise calculation methods are complex and beyond the scope of this overview, but it’s important to consult structural engineers and use appropriate software to ensure the railing meets all safety standards.
Ignoring these calculations can result in a railing that is unsafe and potentially in violation of building codes.
Ultimate Conclusion
Ultimately, selecting the perfect outdoor glass railing involves careful consideration of several factors: the type of glass, the frame material, the overall design aesthetic, and, critically, safety and regulatory compliance. By understanding the different options and their implications, you can create a stunning and secure outdoor space that enhances the beauty and functionality of your property for years to come.
This guide has provided a foundation for your decision-making process; remember to always consult with professionals to ensure a safe and successful installation.