Embark on a journey through the realm of user-centered design, where the user takes center stage in the creation process of innovative products.
Delve into the core principles, methodologies, and real-world applications that shape this design approach.
What is User-Centered Design?
User-Centered Design (UCD) is an iterative design process in which the end-users’ needs, wants, and limitations are given extensive attention at each stage of the product development. It involves understanding the users’ behaviors, preferences, and goals to create products that are intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable to use.
Importance of User-Centered Design
User-Centered Design is crucial in product development as it ensures that the final product meets the users’ expectations and enhances their overall experience. By involving users throughout the design process, companies can create products that are more user-friendly, increase user satisfaction, and reduce the likelihood of costly redesigns after launch.
- One of the most successful products designed with a user-centered approach is the iPhone by Apple. The iPhone revolutionized the smartphone industry by focusing on simplicity, ease of use, and a seamless user experience.
- Another example is the design of Google’s search engine. Google’s minimalist interface and powerful search algorithms were developed with a user-centered approach, making it the most popular search engine globally.
- Amazon’s e-commerce platform is also a great example of user-centered design. The intuitive navigation, personalized recommendations, and easy checkout process have contributed to Amazon’s success in dominating the online retail market.
Principles of User-Centered Design
User-Centered Design is guided by several key principles that prioritize the needs and preferences of the end users throughout the design process. These principles ensure that the final product is intuitive, functional, and enjoyable to use. Let’s delve into some of the fundamental principles of User-Centered Design and how they shape the design process.
1. Empathy
Empathy is at the core of User-Centered Design. Designers must put themselves in the shoes of the users to understand their goals, motivations, and pain points. By empathizing with users, designers can create solutions that truly meet their needs.
2. User Involvement
Involving users in the design process is crucial for creating user-centric products. User feedback and testing help designers identify usability issues and refine their designs accordingly. This iterative approach ensures that the final product resonates with the target audience.
3. Iterative Design
User-Centered Design is an iterative process that involves continuous feedback and refinement. Designers create prototypes, gather user feedback, and make improvements based on that feedback. This cyclical process allows for incremental enhancements and ensures that the final product aligns with user expectations.
4. Usability
Usability is a key principle of User-Centered Design. The focus is on creating products that are easy to use, intuitive, and efficient. Designers strive to eliminate unnecessary complexity and streamline the user experience to enhance usability.
5. Accessibility
Accessibility ensures that products are usable by individuals with diverse abilities. Designers consider factors such as visual impairments, motor disabilities, and cognitive limitations to create inclusive designs that cater to a wide range of users.
Real-World Applications
One real-world application of User-Centered Design principles can be seen in the development of popular mobile applications like Instagram and Airbnb. These platforms prioritize user feedback, conduct usability testing, and iterate on their designs based on user preferences. As a result, they deliver seamless and engaging experiences that resonate with millions of users worldwide.
Understanding User Needs
Understanding user needs is a crucial aspect of user-centered design. By researching and analyzing user needs, designers can create products that truly meet the needs and expectations of the end-users.
Methods for Researching and Understanding User Needs
Researching and understanding user needs involves various methods and techniques to gather valuable insights. Some common approaches include:
- Surveys: Conducting surveys helps in collecting quantitative data about user preferences, habits, and pain points.
- Interviews: Direct interviews with users provide qualitative insights into their behaviors, motivations, and challenges.
- Observation: Observing users in their natural environment can reveal how they interact with products and identify areas for improvement.
- Usability Testing: Testing prototypes with real users helps in identifying usability issues and gathering feedback for iterative design.
By using a combination of these methods, designers can gain a comprehensive understanding of user needs and preferences.
Examples of Tools and Techniques Used to Gather User Insights
Various tools and techniques are employed to gather user insights effectively. Some examples include:
| Heatmaps: | Visual representations of user interactions on a website or app, highlighting areas of interest or confusion. |
| Persona Development: | Creating fictional characters based on user research to represent different user types and their needs. |
| Journey Mapping: | Mapping out the user journey to understand touchpoints, emotions, and pain points throughout the user experience. |
How User Research Influences Design Decisions
User research plays a critical role in shaping design decisions by providing valuable insights that inform the design process. It helps in:
- Identifying user preferences and pain points to address in the design.
- Validating design choices based on user feedback and testing.
- Ensuring that the final product meets the needs and expectations of the target users.
Creating User Personas
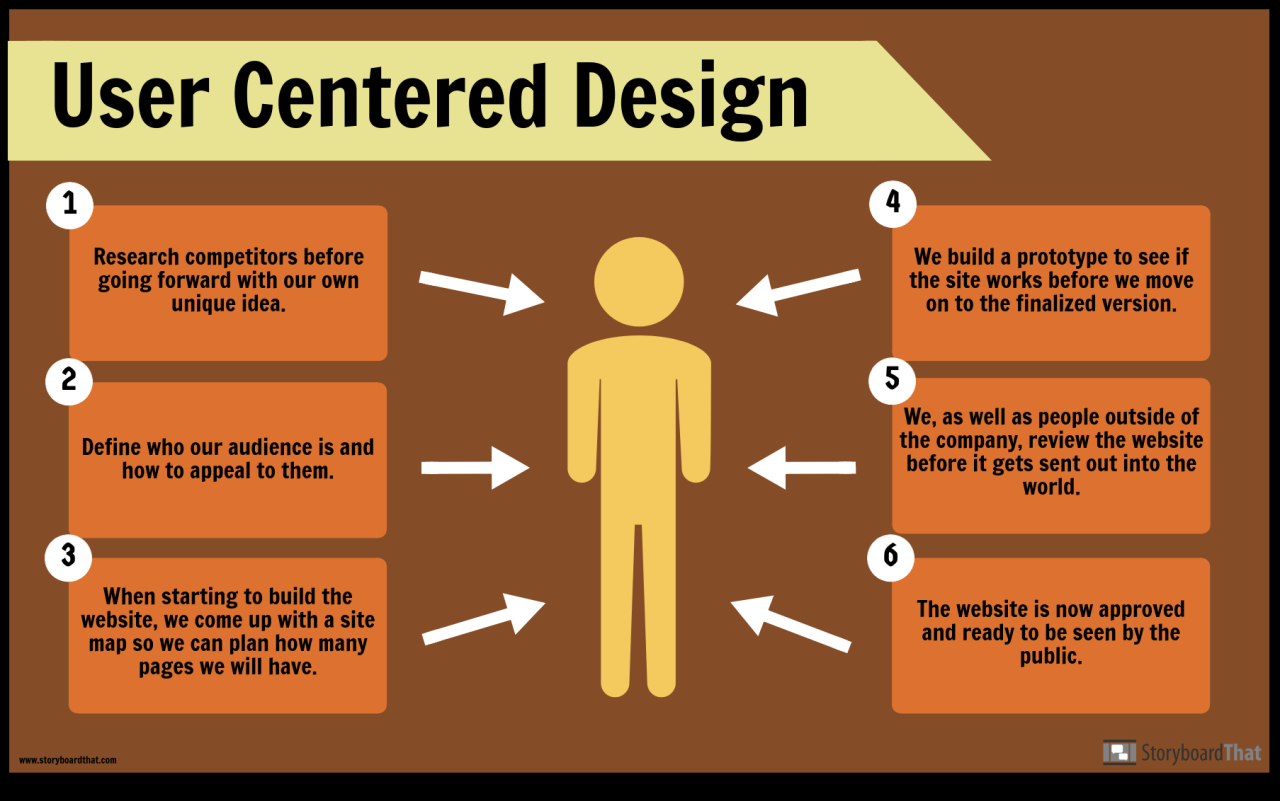
User personas are fictional representations of the key user types for a product or service. They are created based on research and data about real users to help designers understand user needs, goals, behaviors, and preferences. User personas typically include details such as demographics, behaviors, motivations, goals, and pain points.
Importance of User Personas
User personas play a crucial role in the design process by providing a clear understanding of who the target users are. They help designers make informed decisions about features, functionality, and user experience. User personas also enable teams to prioritize design choices based on user needs, ultimately leading to a more user-friendly and effective product.
- User personas help designers empathize with users and design with their needs in mind.
- They guide decision-making by focusing on what matters most to the target audience.
- User personas help ensure that design choices align with user expectations and behaviors.
- They facilitate communication and collaboration among team members by providing a shared understanding of the target users.
Examples of User Personas Impacting Product Design
Example 1: A software company creates user personas for a new project management tool. Through research, they identify two key user personasa busy project manager who needs a streamlined interface and a team member who values collaboration features. This information guides the design team in prioritizing features that cater to these specific user needs.
Example 2: An e-commerce website develops user personas to understand their target customers better. By creating personas representing different age groups, shopping behaviors, and preferences, the design team can tailor the website’s layout, navigation, and product recommendations to provide a personalized shopping experience for each user segment.
Prototyping and Testing
Prototyping and testing are crucial steps in the user-centered design process as they allow designers to gather feedback and make necessary adjustments before finalizing a product or service. Prototypes are early versions of a design that can range from low-fidelity sketches to high-fidelity interactive models.
User testing involves gathering feedback from real users to understand how they interact with the prototype and identify any usability issues.
Types of Prototypes
Prototypes can be categorized into different types based on fidelity and functionality. Low-fidelity prototypes, such as paper sketches or wireframes, are quick and easy to create but may lack detailed functionality. On the other hand, high-fidelity prototypes, like interactive mockups or clickable prototypes, provide a more realistic representation of the final product.
Each type of prototype serves a specific purpose in the design process, helping designers iterate and refine their ideas.
Importance of User Testing
User testing is essential for validating design decisions and ensuring the final product meets user needs and expectations. By observing how users interact with the prototype, designers can identify usability issues, pain points, and areas for improvement. User feedback helps in refining the design, making it more user-friendly and intuitive.
Incorporating user testing throughout the design process leads to a more successful and user-centered product.
Accessibility in User-Centered Design
Accessibility considerations play a crucial role in user-centered design as they ensure that products and services are usable by all individuals, including those with disabilities. By incorporating accessibility features, designers can create inclusive solutions that cater to a diverse range of users.
Importance of Accessibility in Design
Accessibility in user-centered design is essential to ensure that everyone, regardless of ability, can interact with a product or service effectively. It eliminates barriers and enhances the user experience for individuals with disabilities.
- Provide alternative text for images to assist users with visual impairments.
- Implement keyboard navigation to accommodate users who cannot use a mouse.
- Ensure color contrast for readability by users with visual impairments.
- Use clear and concise language to facilitate understanding for users with cognitive disabilities.
Incorporating Accessibility Features
Designers can incorporate accessibility features into product design by following principles such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) and conducting usability testing with individuals with disabilities. By considering accessibility from the outset, designers can create products that are usable by a wider audience.
- Conduct user testing with individuals with disabilities to identify barriers in the design.
- Provide adjustable text size and font options for users with visual impairments.
- Ensure that interactive elements are accessible via keyboard for users who cannot use a mouse.
- Include audio descriptions for multimedia content to make it accessible to users with visual or hearing impairments.
Inclusive Design Practices
Inclusive design practices benefit all users by creating products that are accessible, usable, and enjoyable for everyone. By considering diverse user needs and preferences, designers can develop solutions that accommodate a wide range of abilities.
- Designing for mobile-first to ensure compatibility with different devices and screen sizes.
- Providing multiple ways to navigate and interact with the product, such as voice commands or gestures.
- Offering customizable settings to allow users to personalize their experience based on their preferences.
- Including captions and transcripts for audio and video content to make it accessible to users with hearing impairments.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, user-centered design emerges as a pivotal force driving product development towards user satisfaction and success.