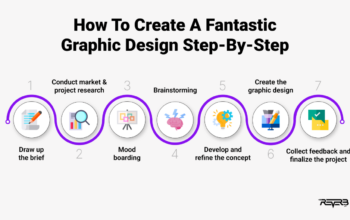
Vector design opens up a world of possibilities in the digital design realm, offering unparalleled flexibility and precision. Dive into the realm of vector graphics as we uncover its unique characteristics and applications, guiding you through a journey of creativity and innovation.
In this guide, we will delve into the nuances of vector design, shedding light on its advantages, techniques, applications, and best practices that shape the landscape of modern design.
Introduction to Vector Design
Vector design is a method of creating digital graphics using mathematical equations to define shapes, lines, and colors. Unlike raster graphics, which are made up of pixels, vector graphics are scalable and can be resized without losing quality. This makes them ideal for logos, illustrations, and other designs that need to be displayed at various sizes.
Key Characteristics of Vector Graphics
- Scalability: Vector graphics can be resized without losing quality, making them versatile for different applications.
- Editable: Shapes and lines in vector graphics are defined by mathematical equations, allowing for easy editing and manipulation.
- Small File Size: Vector files are typically smaller in size compared to raster graphics, making them easier to share and store.
Popular Software for Vector Design
- Adobe Illustrator: A powerful vector design software widely used by professionals for creating logos, illustrations, and other graphic designs.
- CorelDRAW: Another popular vector design tool known for its versatility and user-friendly interface.
- Inkscape: A free and open-source vector graphics editor suitable for beginners and professionals alike.
Advantages of Vector Design
Vector design offers numerous advantages over raster graphics, making it a popular choice for various design projects. One of the key benefits of vector graphics is their scalability, which allows the images to be resized without losing quality. This feature is particularly useful for designs that need to be printed in different sizes or displayed on various devices.
Scalability in Vector Design
Vector graphics are based on mathematical equations rather than individual pixels, allowing them to be scaled up or down infinitely without any loss of clarity or sharpness. This makes vector design ideal for logos, icons, and other graphics that need to maintain their quality across different sizes and resolutions.
High-Quality Prints and Illustrations
Another advantage of vector design is its ability to create high-quality prints and illustrations. Since vector graphics are resolution-independent, they can be printed at any size without pixelation or blurriness. This makes vector design perfect for projects like posters, banners, and marketing materials that require crisp, clear images.
Techniques and Tools for Vector Design
Vector design software offers a wide range of tools and features that allow designers to create stunning illustrations with precision and flexibility. Here, we will delve into some common tools and techniques used in vector design to enhance workflow and productivity.
Common Tools and Features in Vector Design Software
- Pen Tool: A staple in vector design, the pen tool allows for precise control over anchor points and curves.
- Shape Tools: Tools like rectangles, ellipses, and polygons help create basic shapes quickly.
- Gradient Tool: Used to create smooth color transitions, gradients add depth and dimension to designs.
- Layers: Organize elements within a design, making it easier to edit and manage complex illustrations.
Tips for Optimizing Vector Design Workflow
- Use shortcuts: Familiarize yourself with keyboard shortcuts to speed up your workflow.
- Create reusable assets: Save frequently used elements as symbols or presets to easily reuse them in different projects.
- Organize layers: Keep your layers organized and labeled to quickly locate and edit specific elements.
- Utilize grids and guides: Use grids and guides to align elements precisely and maintain consistency in your design.
Popular Techniques for Creating Intricate Vector Illustrations
- Gradient Mesh: Create realistic shading and highlights by using gradient meshes to manipulate color and tone.
- Blend Tool: Blend objects together seamlessly to create smooth transitions and effects.
- Clipping Masks: Use clipping masks to control the visibility of objects and create intricate designs within shapes.
- Pattern Brushes: Apply custom pattern brushes to create intricate borders, textures, and decorative elements.
Applications of Vector Design

Vector design finds extensive applications across various industries, leveraging its scalability and versatility. From branding and marketing to web design and user interface (UI) design, vector graphics play a crucial role in creating visually appealing and professional content.
Branding and Marketing
- Logos: Vector graphics are ideal for creating logos due to their ability to scale without losing quality. Brands can use vector design to ensure their logos look sharp and consistent across different platforms and sizes.
- Marketing Collateral: Brochures, business cards, banners, and other marketing materials benefit from vector design as it allows for easy manipulation of elements and colors for a cohesive brand identity.
- Infographics: Vector graphics are widely used in creating visually engaging infographics that effectively communicate complex information in a clear and appealing manner.
Web Design and User Interface (UI) Design
- Icons and Buttons: Vector icons and buttons are commonly used in web design and UI design due to their ability to be resized without losing quality, ensuring a consistent user experience across devices.
- Illustrations: Websites and apps often incorporate vector illustrations to enhance visual appeal and convey information in a stylized and engaging way.
- Responsive Design: Vector graphics play a key role in responsive design, allowing elements to adapt seamlessly to different screen sizes while maintaining clarity and sharpness.
Differences between Vector and Raster Graphics
Vector and raster graphics are two distinct types of digital images with unique characteristics that differentiate them in terms of scalability, quality, and file formats.
Scalability and Quality
Vector graphics are based on mathematical equations, allowing them to be scaled infinitely without losing quality. This means that whether you resize a vector image to a small icon or a large billboard, it will maintain crisp edges and clarity.
On the other hand, raster graphics are made up of individual pixels, and when resized, the image can become pixelated or blurry, especially when enlarged.
File Formats
Common file formats associated with vector graphics include SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics), AI (Adobe Illustrator), and EPS (Encapsulated PostScript). These formats are ideal for logos, illustrations, and designs that require scalability without loss of quality. Raster graphics, on the other hand, are commonly saved in formats such as JPEG, PNG, and TIFF, which are better suited for photographs and detailed images with complex color variations.
Suitability of Vector Graphics
Vector graphics are more suitable in scenarios where scalability and quality are paramount, such as logo design, typography, and illustrations. They are preferred for tasks that require sharp lines and shapes that can be easily manipulated without loss of quality.
For example, creating a logo that needs to be printed on various materials in different sizes would benefit from being designed as a vector graphic to ensure consistency and sharpness across all applications.
Best Practices for Vector Design
When working on vector design projects, it is essential to follow best practices to ensure efficiency and achieve visually appealing results.
Organizing Layers and Working with Anchor Points
Organizing layers in your vector design software is crucial for maintaining a structured workflow. By grouping similar elements together and naming layers appropriately, you can easily navigate through complex designs. When working with anchor points, practice precision and patience. Adjust handles and curves carefully to achieve smooth and accurate lines in your illustrations.
Creating Efficient and Visually Appealing Vector Illustrations
To create efficient vector illustrations, start by sketching out your ideas on paper before digitizing them. Use the least number of anchor points possible to maintain simplicity in your designs. Experiment with different stroke weights and color palettes to add depth and visual interest to your illustrations.
Importance of File Formats and Exporting Options
Choose the appropriate file format for your vector designs based on the intended use. SVG is ideal for web graphics, while AI or EPS files are suitable for print projects. When exporting vector files, consider the resolution and scale at which the design will be viewed to ensure optimal quality.
Additionally, save multiple versions of your work to have backups and editable files for future modifications.
Last Recap
As we conclude our exploration of vector design, we invite you to embrace the limitless potential of this versatile medium. With its scalability, quality, and practical applications, vector design stands as a cornerstone in the evolution of digital creativity. Let your imagination soar as you harness the power of vectors in your design endeavors.