Visual design is more than just aesthetics; it’s a powerful tool for communication and problem-solving. By harnessing the principles and elements of visual design, you can create impactful designs that engage users and elevate your projects to new heights.
In this guide, we’ll delve into the world of visual design, exploring its role in communication, the tools and techniques that make it shine, and its applications in websites, apps, and real-world projects. Get ready for a captivating journey through the fascinating realm of visual design!
Fundamentals of Visual Design
Visual design is the art of integrating text, images, and graphics to create an engaging, cohesive, and useful interface or product. Its primary role in communication is to deliver messages or information effectively and efficiently through visual aesthetics that appeal to users’ emotions, feelings, and thoughts.Visual design relies on certain principles and elements to establish a strong and clear design.
These principles include balance, contrast, hierarchy, repetition, proximity, and unity. At the same time, the elements used in visual design are line, shape, form, texture, color, and direction.
Principles of Visual Design
Balance: Arranging visual elements symmetrically or asymmetrically, so the design feels stable and even.Contrast: Emphasizing differences between specific visual elements to create a focal point.Hierarchy: Establishing the order of importance of visual elements to help users prioritize and navigate content.Repetition: Applying a consistent visual element throughout the design, such as colors and fonts, to provide continuity.Proximity: Grouping related elements to create a connection and decrease clutter.Unity: Creating harmony and cohesion by visually connecting elements and ideas.
Elements of Visual Design
Line: Shapes or forms that define boundaries and create structure in a design.Shape: Two-dimensional areas defined by lines; shapes can be geometric or organic.Form: Three-dimensional shapes; they can be created through shading, gradient and perspective techniques.Texture: Visual patterns that create sensations of touch and glossiness; they can be actual or implied by varying shading or edges.Color: Psychologically potent visual elements that can attract attention and create mood/feelings.
They influence perception, brand identity, and are critical for visual accessibility.Direction: Movement guides the viewer’s eyes; real or perceived movement through lines, shapes, or images can hold attention.
Impact of Visual Design on User Interface Design and User Experience
Visual design impacts user experience by enabling users to navigate interfaces quickly, access information effortlessly, and retain information more efficiently. It creates a user-friendly product that fosters positive emotions and impressions.By implementing the principles and elements of visual design effectively, visual design establishes a solid interaction foundation for users and products, setting the stage for enjoyable and user-centric experiences.
Visual Design Tools and Techniques
Visual design tools and techniques make up the backbone of the creative process. They enable designers to bring their concepts to life in various ways. The right tools promote efficiency, while techniques refine the overall quality of the design output.
By combining these two elements effectively, designers can enhance their overall workflow.
Popular Visual Design Tools
Design tools can facilitate rapid prototyping, efficient collaboration, and clean visual design. Some of the most-used tools for visual design are:
- Sketch
- Figma
- Adobe XD
- InVision
These tools represent the best of modern visual design, offering vast libraries of UI components, intuitive interfaces, and extensive collaboration capabilities.
Creating a Visual Design Concept or Prototype
The visual design process typically involves several stages:
- Research: Compile information about the project, user personas, and visual references.
- Sketching: Loosely Artikel ideas and concepts without being concerned with details.
- Designing: Construct the layout and visual elements while maintaining consistency and hierarchy.
- Prototyping: Build an interactive prototype to evaluate user experience and flow.
- Iterating: Refine and improve the design based on feedback from stakeholders or user testing.
Throughout these stages, visual design tools can aid designers with features like artboards, layers, reusable components, and rapid design handoff.
Vector-based vs. Raster-based Design Software
Vector-based software (e.g., Sketch, Figma, Illustrator) creates graphics using mathematical equations. These designs retain their quality at any scale and are typically simpler to edit. In contrast, raster-based software (e.g., Photoshop, GIMP) relies on a pixel grid, which leads to lower flexibility and lower resolution as the image scales up.
Collaboration and Communication Tools
Strong collaboration efforts help ensure the success of a design project. Tools like InVision, Figma, and Sketch have built-in features encouraging multi-user workspaces and real-time feedback. As a result, designers create a seamless exchange of ideas and opinions, leading to improved designs.
Version Control and Backup
Incorporating version control in visual design projects helps maintain a clear Artikel of changes made during the development lifecycle. Version control systems
- Allow rollbacks to earlier versions
- Track individual changes
- Facilitate backups
Even if a visual design tool doesn’t come with built-in version control, services like GitHub or GitLab can be used to maintain a design project’s version history.
Visual Design for Websites and Applications
As the digital landscape becomes increasingly diverse, visual design has taken center stage in creating engaging and intuitive web experiences. Successful websites and applications not only boast striking aesthetics but also adhere to accessibility standards and responsive design principles.
Responsive Design Principles
Responsive design allows websites and applications to adapt to different screen sizes and devices while retaining functionality and usability. Implementing a fluid grid system, flexible images, and media queries are best practices for responsive design.
- Fluid grid system: A flexible grid system allows content to adjust according to a user’s screen size. Designers should specify proportions instead of fixed widths to achieve this.
- Flexible images and media: Resizing images and media according to screen size helps maintain aspect ratios along with consistent visual design.
- Media queries: Implementing CSS media queries based on screen width, height, resolution, and orientation offers a more tailored user experience.
Visual Design Evaluation Checklist
When evaluating the visual design of a website or application, consider the following:
- Consistency: Examine the overall aesthetic, ensuring elements such as color palette, typography, and layout are consistent.
- Usability: Check the intuitiveness of navigation, input prompts, and the overall hierarchy of content.
- Responsiveness: Verify adaptability and functionality across multiple devices and browsers.
- Accessibility: Test for color contrast, font sizes, and compatible screen readers.
Examples of Successful Visual Design
- Mobile:Instagram’s minimalistic aesthetic focuses on high-quality imagery, optimized for the mobile experience. This design choice fosters user engagement and contributes to the app’s success.
- Web:Medium’s clean, distraction-free layout showcases content while its intuitive navigation system enhances user experience.
- Wearables:Apple Watch’s compact layout and restrained color scheme optimize functionality and readability while catering to users’ demanding lifestyles.
Accessibility in Visual Design
Accessibility refers to designing products that can be used by people with a diverse range of abilities. Considerations include:
- Color contrast: Ensuring sufficient color contrast facilitates reading for users with visual impairments.
- Font sizes: Selecting legible fonts and providing options to increase text size allows users with visual impairments to better engage with content.
- Screen reader compatibility: Implementing ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) attributes enables interactivity with text-to-speech software for users with visual or reading disabilities.
Visual Design Trends
Visual design trends vary across industries. Tech industries emphasize minimalistic, cutting-edge designs that foster user interaction and personalization. In contrast, e-commerce trends lean toward storytelling and immersive experiences that prompt users to explore and make purchases. Entertainment and education industries typically merge visual narratives with illustrative and didactic content to cater to broader audiences.
Visual Design Process and Methodologies
The visual design process consists of several stages, including research, ideation, prototyping, testing, and refinement. By following a structured process, designers can create effective and user-centered designs. This section will cover the stages of the visual design process, a case study of a visual design project, the importance of creating and maintaining a style guide or design system, and the benefits of conducting usability tests and user interviews.
Additionally, this section will compare design thinking, user-centered design, and agile methodologies in visual design projects.
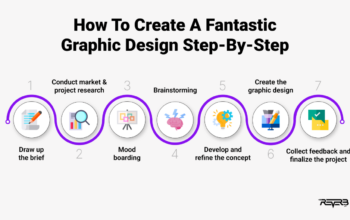
Stages of the Visual Design Process
- Research:The research stage involves gathering information about the target audience, competitors, and industry trends. This stage may include user interviews, surveys, or competitive analysis. The goal of the research stage is to gain a deep understanding of the project’s goals and constraints.
- Ideation:During the ideation stage, designers generate ideas and concepts based on the research findings. This stage may involve sketching, mind mapping, or other ideation techniques. The goal of the ideation stage is to explore a wide range of design possibilities.
- Prototyping:In the prototyping stage, designers create a rough version of the design. This stage may involve creating wireframes, mockups, or prototypes. The goal of the prototyping stage is to test and refine the design concept.
- Testing:During the testing stage, designers gather feedback from users. This stage may involve usability testing, user interviews, or other feedback techniques. The goal of the testing stage is to identify any design issues or areas for improvement.
- Refinement:In the refinement stage, designers make final adjustments to the design based on user feedback. The goal of the refinement stage is to create a polished and user-centered design.
Case Study of a Visual Design Project
Avishek T. worked on a visual design project for a local art gallery. The gallery wanted to create a website that showcased their upcoming exhibitions and allowed users to purchase tickets online. Avishek faced several challenges during the project, including a limited budget, a tight deadline, and a lack of knowledge about the gallery’s target audience.
- Challenges:
- Limited budget
- Tight deadline
- Lack of knowledge about the gallery’s target audience
- Solutions:
- Used affordable visual design tools and techniques
- Allocated time and resources efficiently
- Conducted user research to gain a better understanding of the gallery’s target audience
- Results:
- Created a user-centered website that showcased the gallery’s upcoming exhibitions
- Increased ticket sales and web traffic
- Established a good relationship with the gallery’s management
Style Guides and Design Systems
Creating and maintaining a style guide or design system is essential for any visual design project. A style guide is a set of guidelines that ensure consistency in the use of visual elements such as colors, typography, and imagery. A design system is a more comprehensive and flexible approach that includes design principles, components, and patterns.
By creating a style guide or design system, designers can maintain consistency throughout the design process and ensure that the design meets the project’s goals and constraints.
Design Thinking, User-Centered Design, and Agile Methodologies
Design thinking, user-centered design, and agile methodologies are commonly used in visual design projects. Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that emphasizes empathy, creativity, and experimentation. User-centered design is a design philosophy that puts the user’s needs and preferences at the center of the design process.
Agile methodologies are a set of principles and practices that prioritize flexibility and collaboration. These methodologies can be used separately or in combination to create effective and user-centered designs.
Benefits of Conducting Usability Tests and User Interviews
Conducting usability tests and user interviews can provide valuable insights into the user’s needs and preferences. Usability tests can identify design issues and areas for improvement, while user interviews can provide feedback on the overall user experience. By conducting usability tests and user interviews, designers can make informed design decisions and create a user-centered design.
Visual Design Careers and Opportunities

Visual design is a rapidly growing field with a wide range of career opportunities in various industries. Visual designers are responsible for creating visually appealing and functional designs for websites, apps, marketing materials, and more. As a visual designer, you can work in-house for a company, as a freelancer, or at a design agency, each with its own unique benefits and challenges.
Roles and Responsibilities of Visual Designers
Visual designers play a crucial role in shaping the look and feel of a brand or product. They are responsible for creating visually appealing designs that effectively communicate a message or idea to a target audience. This can include creating visual elements such as logos, icons, and illustrations, as well as designing layouts for websites, apps, and other digital interfaces.Visual designers must have a strong understanding of the principles of design, including typography, color theory, and composition.
They must also be skilled in various design tools and techniques, including Adobe Creative Suite, Figma, and Sketch, to create visually stunning designs that meet the needs of their clients or employers.
Importance of Networking and Self-Promotion for Visual Designers
Networking and self-promotion are essential for visual designers looking to advance their careers and build their professional networks. Attending industry events, joining online communities, and sharing your work on social media are all great ways to connect with other designers and potential employers.Having an online portfolio that showcases your best work is crucial for self-promotion as a visual designer.
This can include a personal website, a Behance or Dribbble profile, or a LinkedIn page that highlights your skills and experience. Networking and self-promotion can help you land new clients, job opportunities, and collaborations with other designers.
Resources for Continuous Learning and Skill Development
Continuous learning and skill development are essential for visual designers looking to stay up-to-date with the latest design trends and technologies. There are many resources available for visual designers to continue learning and improving their skills, including:
- Online courses: Websites such as Udemy, Skillshare, and LinkedIn Learning offer a wide range of courses on visual design, from beginner to advanced levels.
- Forums and communities: Online forums and communities, such as Designer Hangout and Reddit’s r/design_critiques, are great places to connect with other designers, get feedback on your work, and learn new techniques and approaches.
- Books and blogs: Books and blogs on visual design, such as “Don’t Make Me Think” by Steve Krug and “The Elements of User Experience” by Jesse James Garrett, can provide valuable insights and inspiration for visual designers.
In-House vs. Freelance Visual Design Work
In-house visual designers work for a specific company, creating designs for their products or services. Freelance visual designers, on the other hand, work for multiple clients on a project-by-project basis.In-house visual designers typically have a steady stream of work and a consistent paycheck, as well as the benefits of working for a larger organization.
However, they may have less creative freedom and may be limited in the types of projects they can work on.Freelance visual designers have more creative freedom and flexibility in the types of projects they can work on, as well as the ability to set their own rates and work hours.
However, they may have less job security and have to spend more time marketing themselves and finding new clients.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Visual Design Careers
Emerging technologies, such as virtual and augmented reality, are having a significant impact on the field of visual design. Visual designers must stay up-to-date with these new technologies and learn how to create designs that are optimized for these new interfaces.Virtual and augmented reality offer new opportunities for visual designers to create immersive and interactive designs that engage users in new and exciting ways.
As these technologies continue to evolve, visual designers will need to stay on the cutting edge of these trends to remain relevant and competitive in the field.
Summary
Visual design has the power to transform user experiences and revolutionize the way we interact with digital and physical products. As you’ve learned, a strong understanding of its principles, elements, and best practices can help you create impactful designs that resonate with users and achieve your goals.
Keep refining your skills and stay curious about emerging trends and technologies in visual design – the possibilities are truly boundless!